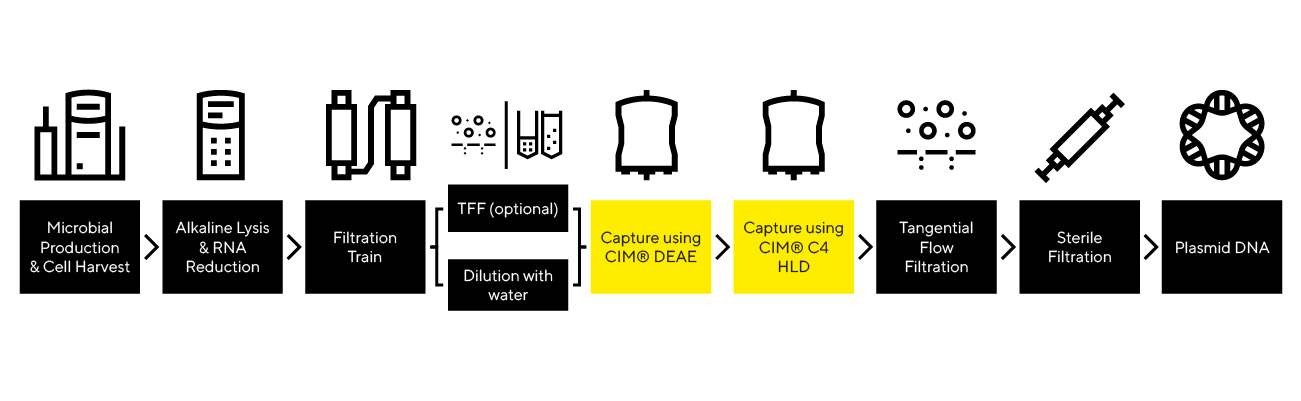
Cornerstone Process Development Services for plasmid DNA (pDNA) production support the internal establishment of plasmid production processes at customer sites, ensuring compliance with regulatory purity specifications. Development is conducted at up to 10-liter bioreactor scale, including fermentation (if required), lysis optimization at up to 10-liter bioreactor scale, clarification, TFF, chromatography, and sterile filtration.
SOPs for all unit operations transferred to the customer. Hands-on training is provided in Cornerstone Laboratories, covering fermentation (if needed), lysis , clarification, TFF, chromatography, and sterile filtration.
DOE methodology, coupled with chromatographic purity analysis and productivity monitoring, is utilized to maximize recovery and optimize downstream purification. Additionally, plasmid DNA linearization is offered to meet specific project requirements. Detailed reports with results and SOPs are included to ensure seamless integration and operational excellence.
Addressing the Challenges in pDNA Process Development
Lysis
Scaling up bacterial lysis poses challenges due to the need for precise control over the duration of exposure to NaOH, which is challenging to manage in batch approach, particularly at large scale. Extended exposure of bacterial cells to a strong base and shear forces can cause fragmentation of host cell genomic DNA and shearing or nicking of the supercoiled (SC) plasmid, results in open-circular (OC) DNA. Both are critical impurities that must be removed in the downstream process.

Cornerstone® Solution
In-line/continuous lysis with Alkalizator offers precise control over cell exposure to NaOH during cell lysis through flow adjustment and efficient neutralization of lysed cells by an in-line static mixer. This approach enhances robustness and improves the contaminant profile, including genomic DNA and isoform homogeneity.

Role of Analytics
To monitor the efficiency of alkaline lysis, rapid at-line chromatographic analytics is employed. The PATfix pDNA platform with the CIMac pDNA analytical method quantifies the main pDNA isoforms (SC, OC, linear – LIN, and multimers) and detects the presence of RNA and other impurities. This chromatographic method offers the advantage of simple sample preparation through dilution with appropriate buffers, unlike other methods that are either not quantifiable (AGE) or require impractically large sample volumes to for detection of impurities(CE). Given the complexity of lysis process, a design-of-experiment (DOE) approach using MODDE® software is typically used to define the design space. CIMac pDNA enables the separation and quantification of sample components, including unbound impurities (e.g., proteins), weakly bound host-cell RNA, and plasmid DNA isoforms (OC, LIN, SC, MM). This provides insights into the efficiency of lysis (mass of plasmid extracted per mass of cell paste, relative to the mass of RNA) and the quality of the extracted pDNA (e.g., degree of open-circular isoform generated during lysis).
Tangential Flow Filtration (TFF)
Optimizing the TFF step is essential to achieve high product recovery and the desired final concentration while minimizing the time required.

Cornerstone® Solution
For buffer exchange and concentration of chromatographically purified pDNA into the final formulation buffer, single-use TFF membranes of various sizes (e.g., 50 cm², 200 cm²) and pore sizes (e.g., 50 kDa, 100 kDa) are used to accommodate different molecule sizes and initial sample volumes. To optimize this step, a TFF system like the Sartoflow® Smart TFF System is employed to develop a scalable TFF process.
pDNA Capture Step
Purifying plasmid DNA is difficult due to its large size and sensitivity to shear forces. Prolonged exposure to lysate conditions can degrade supercoiled pDNA, requiring rapid processing.

Cornerstone® Solution
The capture of pDNA from the lysate is accomplished using the weak anion exchange column CIMmultus® DEAE (scalable from 1 mL to 40 L column volume), ideal for pDNA processing due to its low shear forces. This column effectively removes most host cell RNA and proteins while concentrating multiple plasmid DNA isoforms (OC, SC, multimers) in the eluate. The plasmid DNA in the eluate is stable and can be stored for extended periods if necessary. DEAE offers high dynamic capacity and excellent recovery rates.

Role of Analytics
The CIMac pDNA column serves as an analytical tool for pDNA analysis, enabling the quantification of all pDNA isoforms and monitoring degradation products and the removal of impurities such as RNA throughout the entire process.
pDNA Polishing Step
Achieving regulatory purity of target molecules requires the elimination of unwanted pDNA isoforms (OC pDNA) and residual impurities, including host cell RNA, genomic DNA, proteins, and endotoxins.

Cornerstone® Solution
The polishing step utilizes the CIMmultus® C4 HLD column with a Selective Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography (SHIC) approach, effectively eliminating OC pDNA and gDNA in the flow-through. This method is highly selective for enriching supercoiled pDNA, achieving a purity of over 95%. The column also efficiently removes endotoxins, residual RNA, and proteins, which remain bound to the column after elution of the target molecules. This process is crucial for meeting regulatory specifications for plasmid DNA vaccines and other therapeutic applications.

Role of Analytics
The removal of unwanted pDNA isoforms and residual host cell RNA can be monitored using the CIMac pDNA analytical method.
Sterile Filtration
Preventing microbial contamination and ensuring patient safety with sterile filtration solutions suitable for large, shear-sensitive pDNA molecules.

Cornerstone® Solution
The Sartopore family of filters is used for sterile filtration, offering a broad range of PES membrane combinations with a 0.2 µm final membrane pore size. These filters can be integrated into filter transfer sets for closed single-use applications.
Hear from Our Customers
Ready to Discuss the Project?
FAQ About pDNA Process Development Services
- 2µm channel size: 4-6 mg/mL
- 6µm channel size: 1 mg/m
CIMac pDNA can separate different pDNA isoforms (oc, sc, and lin), but the retention time difference between different pDNA sizes is minimal.
Yes, with CIMac pDNA we can detect residual RNA in samples.
CIMac pDNA analytics can aid our linearization optimization processes by informing us when the reaction is complete and no SC pDNA remains.
We generally recommend using the 1.4 µm channels (analytics) or 2 µm channels (preparative) for plasmids up to 7-8 kbp. For larger plasmids we use 6.0 µm channel sizes columns.
Consult Our Experts
Our experts would be happy to discuss your project. Fill the contact form below or send us an email to cornerstone@biaseparations.com




