AAV
Non-affinity AAV Manufacturing Process. Overview of Solutions for Purification and Analytics.
Purification of AAV using monolithic columns is one of the key purification process solution in gene therapy industry. Non-affinity industrial manufacturing purification platform for AAV is based on two chromatographic steps – cation exchange capture and full AAV capsid enrichment based on anion exchange or multimodal interaction. Click here to learn more about the latest improvements in Empty-full AAV peak separation through the novel QA Empty-full method and the best reproducibility in chromatography using of CIMmultus QA HR columns.
Besides chromatography, sample pre-treatment before entering the capture step is of a great importance, because it contributes to higher capacity of the capturing columns and higher purity of the final product.
To enable fast process development and in-process control fast, reliable and cost-efficient analytics using high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) is needed.
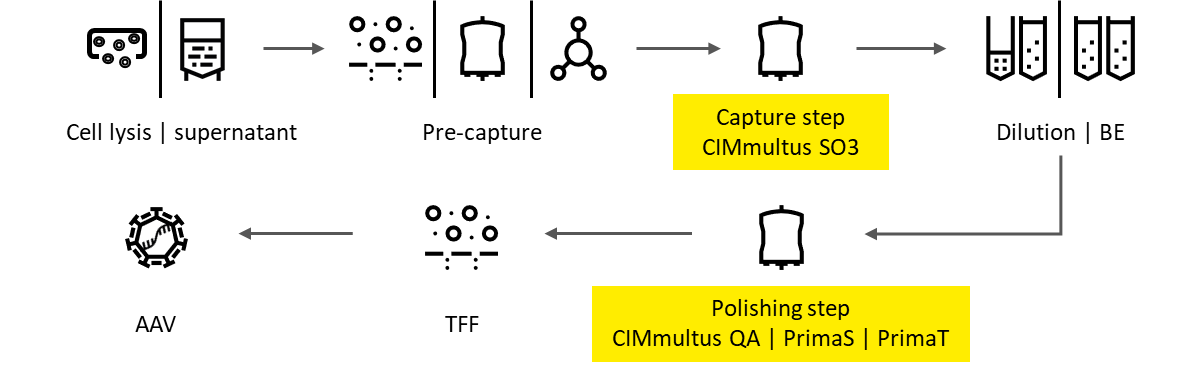
Downstream processing of a complex AAV sample
Therapeutic applications of AAV-based gene therapy vectors require the removal of process and product related impurities, as they represent serious safety threats as well as burden the economics of manufacturing.
The most critical subset of process related impurities includes: Host cell impurities (e.g. hcDNA, hc proteins, chromatin complexes), plasmid(s), transfection reagents.
The most critical subsets of product related impurities: Non-potent AAV capsids (empty AAV, partially filled AAV, AAV capsid containing hcDNA insert), capsid-capsid complexes and capsid-DNA complexes.
Sartorius BIA Separations has developed fully scalable monolith-based AAV DSP platforms to eliminate process specific and product specific impurities.
Pre-capture– Reduction of chromatin, host cell DNA and host cell proteins
Downstream starts with collection of supernatant or lysis material of the cell culture. The main goal of pre-capture step is to reduce host cell impurities as soon as possible in the process to prevent further formation of AAV-chromatin complexes.
Chromatin exhibits charge characteristics to form complexes with any material including the AAV. These complexes occupy binding sites on chromatographic columns. In addition, host cell DNA located inside chromatin structures is harder to detect and quantify. This hidden threat can also trigger undesirable side effects in patient’s body due to their high oncogenic and infectivity potential. Pre-capture step therefore significantly improves product purity and column capacity.
TFF is usually used for the pre-capture step, but to achieve the best process yield and product purity one should test a wide toolbox of pre-capture methods or, if sample is very complex, even a combination of them, including: OH chromatography, flocculation, TFF, solid phase extraction, precipitation and/or nuclease treatment.
Acidic precipitation of impurities is part of the AAV process when strong cation exchanger is used as capture step.
CIMmultus™ SO3 capture is the core of the AAV purification
Example of CIMmultus SO3 chromatogram
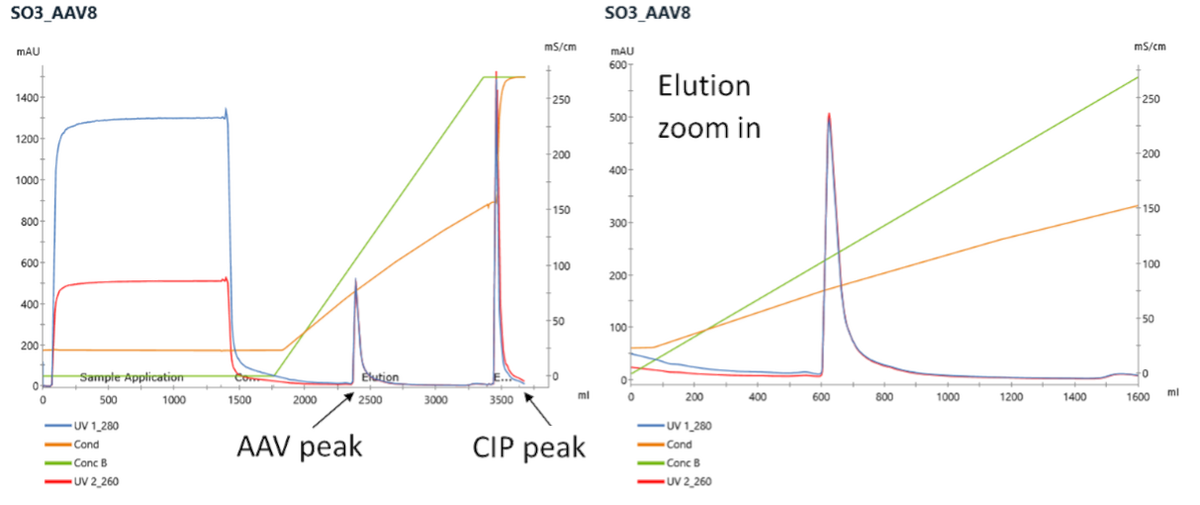
Capture using cation exchange CIMmultus™ SO3 column is performed at acidic pH (3.5 – 4.5) to remove most of hcDNA and hc proteins impurities while concentrating AAV to target concentration (1E13 to 5E13 vg/ml). This process works with all serotypes tested to date.
- High recovery of potent capsids, since loading and elution of the AAV from the SO3 column happens at higher pH (pH 3.5 or higher) resulting in lower manufacturing costs
- Most of the chromatin complexes are removed by CIP, and most of the small protein impurities are in flowthrough during the sample application step resulting in better performance of the polishing step
- High binding capacity (from 1E12 to more than 1E14 vg/ml, depending on sample preparation) resulting in lower manufacturing costs
- High resolution, similar to affinity ligands
- Easy scale-up
- Binds any serotype
- Very fast at any scale (flow rates of >1CV/min)
- Reusable column (cleanable with 1M NaOH) resulting in lower costs of goods
- No shear stress resulting in higher product yield
CIMmultus™ QA HR polishing enables full AAV capsid enrichment
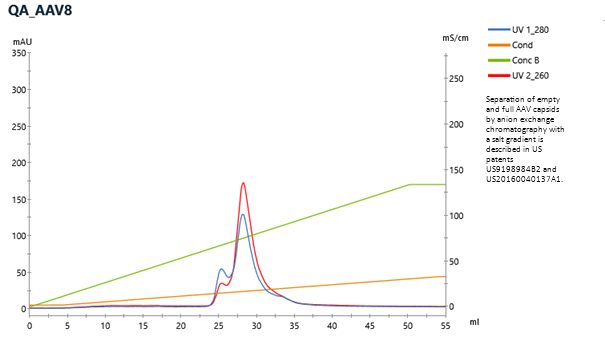
Quaternary amine is well known ligand for separation of empty and full capsids. CIMmultus™ QA HR column exploits anion exchange mechanism, while elution is usually achieved with ascending salt concentration. Presence of magnesium has an effect on empty elution and removal.
- High binding capacities (1E13- more than 2E14 vg/ml of monolith), depending on initial empty to full ratio
- Allows for >90% full capsid with most of the serotypes if empty/full ratio of the sample is at about half:half
- Binds any serotype
- Sample loading at low conductivity (2-5 mS/cm)
- Effective pH: 8.5 – 9.5
- Reusable (cleanable with 1M NaOH)
- No shear stress
For AAV application CIMmultus QA HR column with firmer release criteria and speCIMen for enhanced reproducibility of AAV empty-full separation is going to be provided.
Alternative Polishing using novel ligands
If CIMmultus QA HR does not provide satisfactory full AAV enrichment or the IP is of concern novel ligands shall be tested. At present CIMmultus PrimaS and CIMmultus PrimaT are available.
CIMmultus™ PrimaS for AAV
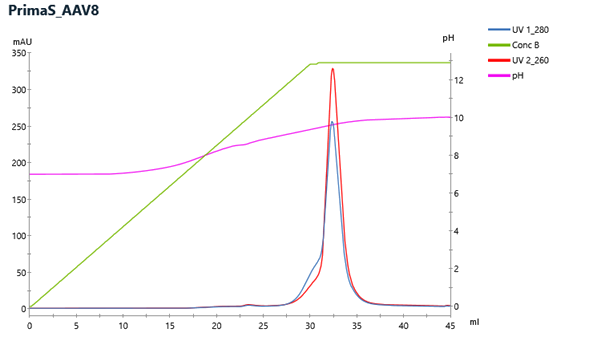
PrimaS is multimodal ligand with weak-anion exchange and hydrogen-bonding interactions provides different selectivity compared to the CIMmultus QA HR ligand. Elution is usually with ascending pH gradient and constant conductivity. For AAV application CIMmultus PrimaS column with firmer release criteria and speCIMen for enhanced reproducibility of AAV empty-full separation is going to be provided.
CIMmultus™ PrimaT
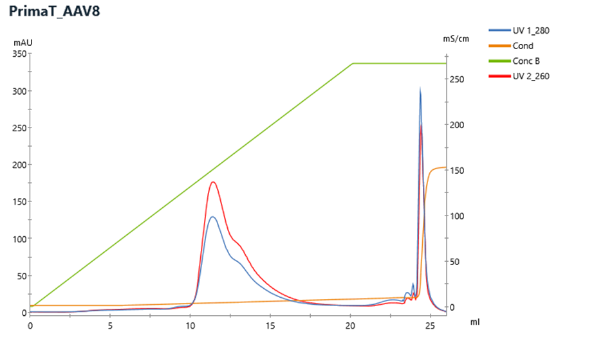
PrimaT is a multimodal ligand with weak-anion exchange, hydrogen-bonding and metal affinity interactions. Two different approaches are recommended for the elution of AAV capsids: first, a linear MgCl2 gradient where the full AAV particles elute and then a high salt wash step where most of the empty particles elute. For AAV application CIMmultus PrimaT column with firmer release criteria and speCIMen for enhanced reproducibility of AAV empty-full separation is going to be provided.
Fast process development and in-process control require orthogonal and high-performance analytics
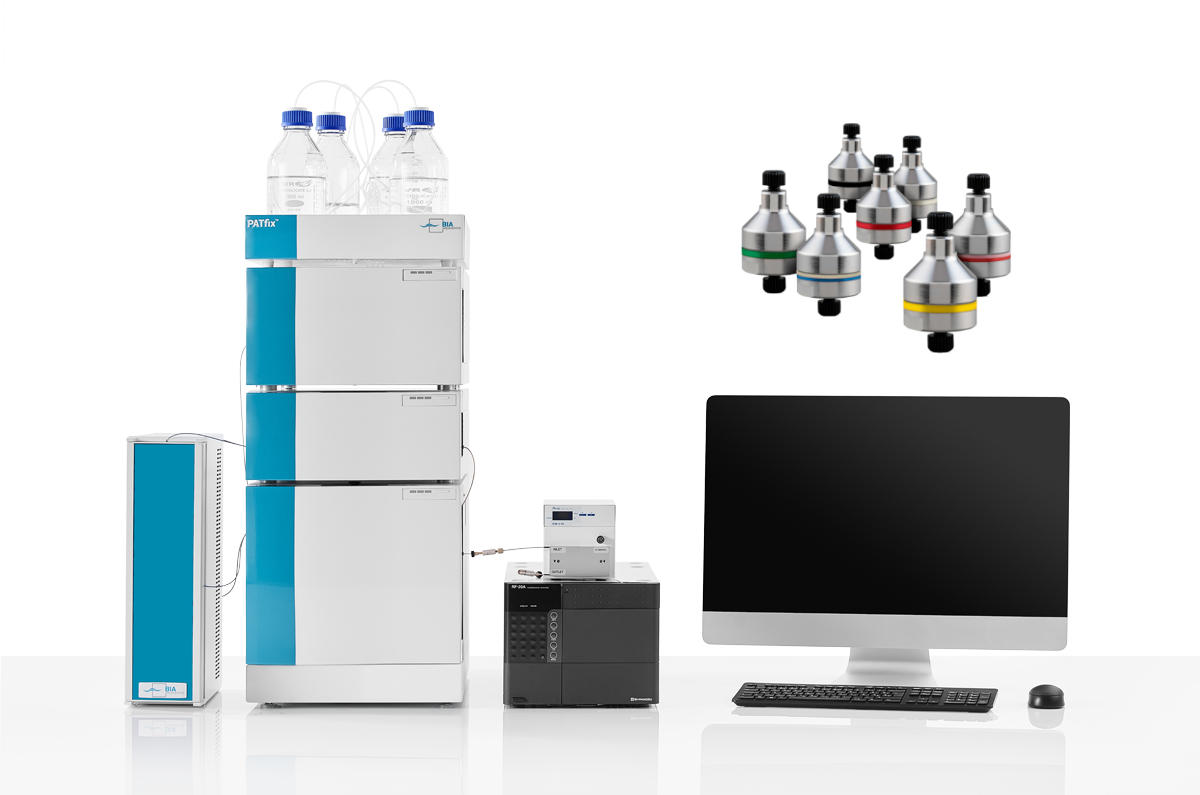

Rapid HPLC analysis of AAV fractions removes a bottleneck for fast process development. Sartorius BIA Separations has developed HPLC system PATfix™, specifically designed for the analysis of large biomolecules and in-process control of upstream and downstream processing steps.
Made of biocompatible materials, the PATfix™ system is equipped with a triple detector setup (UV, fluorescence and MALS) and is suitable for the analysis of complex AAV samples. Conductivity and pH monitors are included to support robust analytics. The system comes with next generation PATfix™ software, particularly adapted for multidetector data processing.
In combination with the analytical CIMac™ columns, the PATfix™ system can achieve cutting-edge sample characterisation in a single chromatographic run just in a few minutes. Combined with orthogonal methods, e.g. ddPCR, ELISA, AUC, cryoTEM, it offers a versatile & robust analytical toolkit that meets the challenges of gene therapy viral vectors production.
Sartorius BIA Separations has developed a broad portfolio of HPLC based analytical methods for fast, accurate, and meaningful characterization of:
- Mammalian or Insect cell culture harvests
- Intermediate / in-process samples at any unit-operational step
- Purified AAV vector lots
Applications of novel CIMac™ based HPLC column protocols employing innovative, orthogonal detector assemblies allow for holistic interpretation of samples, with respect to:
- Impurity profile
- Host cell DNA burden
- Total AAV content (CIMac™ SO3-0.1 Analytical Column)
- Full/Empy Capsid ratios (CIMac™ AAV empty/full-0.1 Analytical Column)
- Free - and Capsid-associated DNA
For quantification of total AAV titre, cation-exchange CIMac™ SO3 is the column of choice. Cation exchange does not separate empty and full capsids and is therefore perfect for total capsid titre. This column is also used to measure overall mass balance - we analyse each fraction or step in the process and compare the peak areas to calculate recoveries. For early stage DSP samples with more impurities, a light scattering detector is recommended.
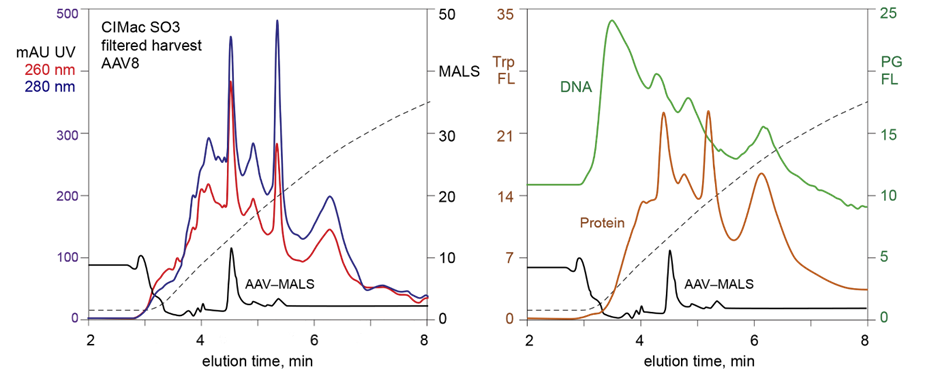
For AAV empty-full analysis Sartorius BIA Separations offers 3 different chemistries: CIMac™ AAV E/F column (QA based ligand optimized for AAV separation), CIMac™ PrimaS (AAV) and CIMac™ PrimaT (example chromatograms of AAV8 using CIMac™ empty-full columns).
Testimonial
“Andelyn Biosciences has regularly worked with BIA monolithic chromatography columns in our lab scale and scale up process development programs. We were delighted to consult with the Sartorius BIA Separations team by providing advice on the development of an AAV harvest capture methodology that was recently published in the journal Electrophoresis. We’re excited to see the continuous innovation in chromatography separations for gene therapy applications.”
Samir Acharya, AD of Process Development, Andelyn Biosciences
